DATA MINING
WHAT IS DATA MINING?
In simple terms data mining is knowledge from Tera bytes or Peta bytes data.
we have vast amount of data collected daily. Analysing such data is important need.Data mining provides tools to discover knowledge from data.
examples of huge data: data for business,engineering,medicine etc.
FACT: "Facebook revealed some big, big stats on big data to a few reporters at its HQ today, including that its system processes 2.5 billion pieces of content and 500+ terabytes of data each day. It's pulling in 2.7 billion Like actions and 300 million photos per day, and it scans roughly 105 terabytes of data each half hour".Facebook uses hadoop tool for managing data
As there is explosive growth of available data there is an emergency of powerful and versatile tools that are badly needed to uncover valuable information from tremendous data and to transform such data to knowledge.
---->Google Flue Trend is a popular example that reveals how data minig can be helpful in meeting current global challenges.
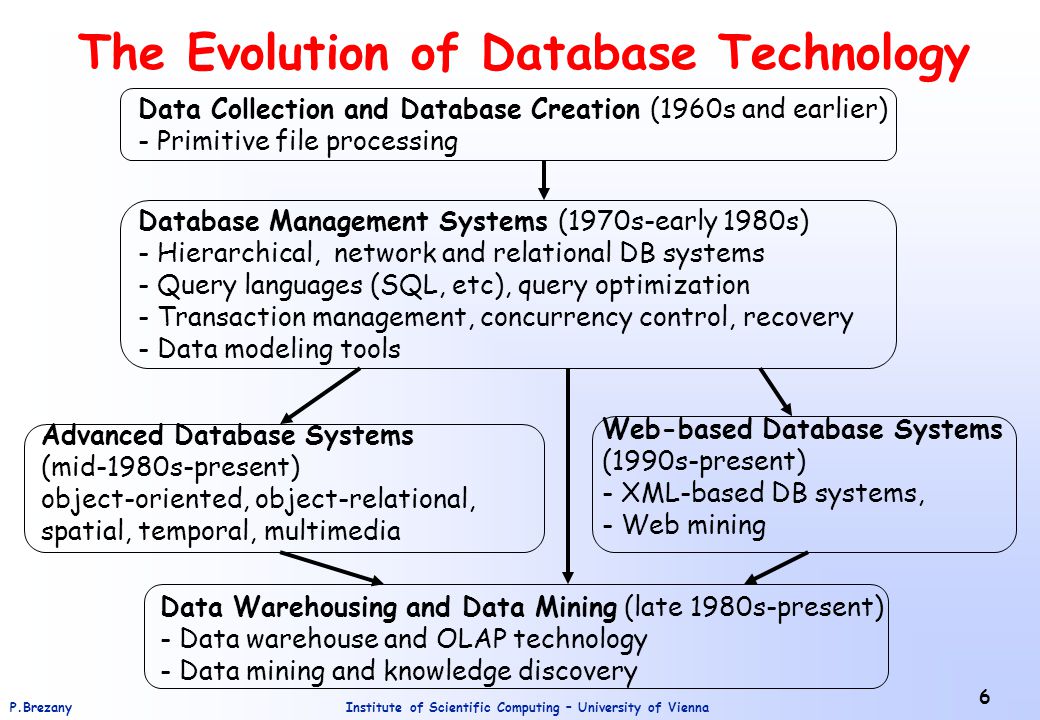
EVOLUTION OF DATABASE SYSTEM:As shown below there were sources which can mange small amount of transaction and model data at the start.Now transformed to data warehousing and mining.

SO HOW DATA MINING WORKS? {lets say it process of gaining knowledge}
important terms: 1)data cleaning-cleaning unwanted and inconsistent data that are more often redundant and burden to the process.
2)data integration-multiple sources of data can be combined and which tend to generate knowledge.
3)data selection- data relevant to analysis task are retried from database.
4)data transformation-data are transformed and consolidated into forms appropriate for aggregation.
5)data mining-methods applied to identify patterns that represent knowledge.
6)data representation-visual and representation techniques are used to present mined data.
Steps in process of knowledge from huge data:

WHAT KIND OF DATA CAN BE MINED?
https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/data-mining-sources-of-data-that-can-be-mined/
above link is best source on what data can be mined.
WHAT KIND OF PATTERNS CAN BE MINED?
Data mining functionalities are used to specify kinds of patterns to be found in data mining tasks.In general such tasks are classified to two categories:descriptive and predictive.Descriptive mining characterise properties of data into target data.predictive data can perform induction on current data to make predictions.
In simple terms data mining is knowledge from Tera bytes or Peta bytes data.
we have vast amount of data collected daily. Analysing such data is important need.Data mining provides tools to discover knowledge from data.
examples of huge data: data for business,engineering,medicine etc.
FACT: "Facebook revealed some big, big stats on big data to a few reporters at its HQ today, including that its system processes 2.5 billion pieces of content and 500+ terabytes of data each day. It's pulling in 2.7 billion Like actions and 300 million photos per day, and it scans roughly 105 terabytes of data each half hour".Facebook uses hadoop tool for managing data
As there is explosive growth of available data there is an emergency of powerful and versatile tools that are badly needed to uncover valuable information from tremendous data and to transform such data to knowledge.
---->Google Flue Trend is a popular example that reveals how data minig can be helpful in meeting current global challenges.
EVOLUTION OF DATABASE SYSTEM:As shown below there were sources which can mange small amount of transaction and model data at the start.Now transformed to data warehousing and mining.


SO HOW DATA MINING WORKS? {lets say it process of gaining knowledge}
important terms: 1)data cleaning-cleaning unwanted and inconsistent data that are more often redundant and burden to the process.
2)data integration-multiple sources of data can be combined and which tend to generate knowledge.
3)data selection- data relevant to analysis task are retried from database.
4)data transformation-data are transformed and consolidated into forms appropriate for aggregation.
5)data mining-methods applied to identify patterns that represent knowledge.
6)data representation-visual and representation techniques are used to present mined data.
Steps in process of knowledge from huge data:

WHAT KIND OF DATA CAN BE MINED?
https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/data-mining-sources-of-data-that-can-be-mined/
above link is best source on what data can be mined.
WHAT KIND OF PATTERNS CAN BE MINED?
Data mining functionalities are used to specify kinds of patterns to be found in data mining tasks.In general such tasks are classified to two categories:descriptive and predictive.Descriptive mining characterise properties of data into target data.predictive data can perform induction on current data to make predictions.
- Data Characterisation − This refers to summarising data of class under study. This class under study is called as Target Class.
- Data Discrimination − It refers to the mapping or classification of a class with some predefined group or class.
Mining of Frequent Patterns
Frequent patterns are those patterns that occur frequently in transactional data. Here is the list of kind of frequent patterns −- Frequent Item Set − It refers to a set of items that frequently appear together, for example, milk and bread.
- Frequent Subsequence − A sequence of patterns that occur frequently such as purchasing a camera is followed by memory card.
- Frequent Sub Structure − Substructure refers to different structural forms, such as graphs, trees, or lattices, which may be combined with item-sets or subsequences.
Mining of Association
Associations are used in retail sales to identify patterns that are frequently purchased together. This process refers to the process of uncovering the relationship among data and determining association rules.For example, a retailer generates an association rule that shows that 70% of time milk is sold with bread and only 30% of times biscuits are sold with bread.Mining of Correlations
It is a kind of additional analysis performed to uncover interesting statistical correlations between associated-attribute-value pairs or between two item sets to analyze that if they have positive, negative or no effect on each other.Mining of Clusters
Cluster refers to a group of similar kind of objects. Cluster analysis refers to forming group of objects that are very similar to each other but are highly different from the objects in other clusters.Classification and Prediction
Classification is the process of finding a model that describes the data classes or concepts. The purpose is to be able to use this model to predict the class of objects whose class label is unknown. This derived model is based on the analysis of sets of training data. The derived model can be presented in the following forms −- Classification (IF-THEN) Rules
- Decision Trees
- Mathematical Formulae
- Neural Networks
The list of functions involved in these processes are as follows −- Classification − It predicts the class of objects whose class label is unknown. Its objective is to find a derived model that describes and distinguishes data classes or concepts. The Derived Model is based on the analysis set of training data i.e. the data object whose class label is well known.
- Prediction − It is used to predict missing or unavailable numerical data values rather than class labels. Regression Analysis is generally used for prediction. Prediction can also be used for identification of distribution trends based on available data.
- Outlier Analysis − Outliers may be defined as the data objects that do not comply with the general behavior or model of the data available.
- Evolution Analysis − Evolution analysis refers to the description and model regularities or trends for objects whose behavior changes over time.
Data Mining Task Primitives
- We can specify a data mining task in the form of a data mining query.
- This query is input to the system.
- A data mining query is defined in terms of data mining task primitives.
Note − These primitives allow us to communicate in an interactive manner with the data mining system. Here is the list of Data Mining Task Primitives −- Set of task relevant data to be mined.
- Kind of knowledge to be mined.
- Background knowledge to be used in discovery process.
- Interestingness measures and thresholds for pattern evaluation.
- Representation for visualizing the discovered patterns.
Set of task relevant data to be mined
This is the portion of database in which the user is interested. This portion includes the following −- Database Attributes
- Data Warehouse dimensions of interest
Kind of knowledge to be mined
It refers to the kind of functions to be performed. These functions are −- Characterization
- Discrimination
- Association and Correlation Analysis
- Classification
- Prediction
- Clustering
- Outlier Analysis
- Evolution Analysis
Background knowledge
The background knowledge allows data to be mined at multiple levels of abstraction. For example, the Concept hierarchies are one of the background knowledge that allows data to be mined at multiple levels of abstraction.Interestingness measures and thresholds for pattern evaluation
This is used to evaluate the patterns that are discovered by the process of knowledge discovery. There are different interesting measures for different kind of knowledge.Representation for visualizing the discovered patterns
This refers to the form in which discovered patterns are to be displayed. These representations may include the following. −- Rules
- Tables
- Charts
- Graphs
- Decision Trees
- Cubes


Comments
Post a Comment